In the modern financial landscape, credit scoring systems play a pivotal role in determining an individual’s financial health and their access to various services such as loans, credit cards, and mortgages. Yet, despite their ubiquity, many individuals are unaware of the intricacies that govern these systems. In this blog post, we delve into the depths of credit scoring systems, exploring what they are, how they work, and why they matter.
Table of Contents
What is a Credit Scoring System?
A credit scoring system is essentially a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness. It is a tool used by lenders to assess the risk associated with extending credit to a borrower. The score is based on various factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and new credit inquiries.
How Do Credit Scoring Systems Work?
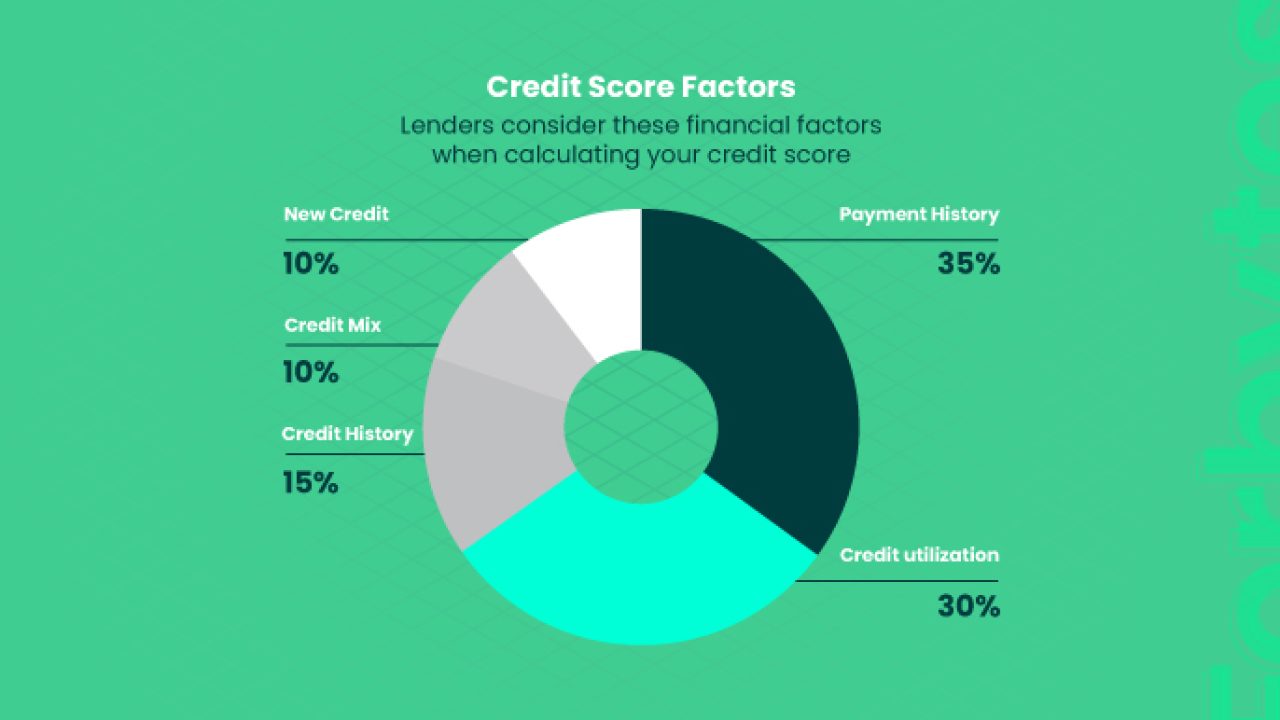
Credit scoring systems employ complex algorithms to analyze an individual’s credit report and assign them a numerical score. While the exact algorithms used may vary between different scoring models (such as FICO Score and VantageScore), they generally consider similar factors.
1. Payment History: This is one of the most critical factors in determining a credit score. It evaluates whether you have paid your bills on time and in full. Late payments can significantly lower your score.
2. Credit Utilization: This refers to the percentage of your available credit that you are currently using. Keeping this ratio low is advisable, as high credit utilization can indicate financial strain.
3. Length of Credit History: The length of time you’ve had credit accounts open can impact your score. Generally, a longer credit history is viewed more favorably by lenders.
4. Types of Credit: Lenders like to see a mix of credit types, such as credit cards, mortgages, and installment loans, in your credit history. It demonstrates your ability to manage different types of credit responsibly.
5. New Credit Inquiries: Opening several new credit accounts in a short period can raise concerns about your financial stability and lower your score.
Why Do Credit Scores Matter?
Credit scores wield significant influence over an individual’s financial life. They can determine whether you qualify for a loan or credit card, the interest rates you’ll pay, and even your ability to rent an apartment or secure certain jobs.
A high credit score opens doors to better financial opportunities, such as lower interest rates and higher credit limits, while a low credit score can lead to rejections or unfavorable terms.
Tips for Improving Your Credit Score
If you’re looking to improve your credit score, there are several strategies you can employ:
- Pay Your Bills on Time: Consistently paying your bills on time is one of the most effective ways to boost your credit score.
- Reduce Credit Card Balances: Aim to keep your credit card balances low relative to your credit limits.
- Limit New Credit Applications: Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts within a short period, as this can negatively impact your score.
- Monitor Your Credit Report: Regularly check your credit report for errors and address any discrepancies promptly.
- Maintain a Diverse Credit Mix: If possible, maintain a mix of credit types in your history to demonstrate responsible credit management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, credit scoring systems are integral to the modern financial landscape, shaping individuals’ access to credit and financial opportunities. Understanding how these systems work and taking proactive steps to manage your credit responsibly can have a profound impact on your financial well-being. By staying informed and implementing sound financial practices, you can navigate the world of credit with confidence and achieve your long-term financial goals.